简单例子
先根据官网例子尝试核心功能是否能走通。
# 添加临时环境变量Path,让程序能正确找到Graphviz软件。
# 在Windows设置"修改环境变量"窗口中查看环境变量Path。或在Python交互式解释器中查看os.environ["PATH"]的值。
# 即使已经添加环境变量,但代码并没有自动找到程序,经过测试还是添加临时环境变量能成功和简单。
# 添加路径应该与安装路径一致。路径不对或软件未安装将报错报错"make sure the Graphviz executables are on your systems"。
import os
import graphviz
os.environ["PATH"] += ';' + r'C:\Program Files\Graphviz\bin'
# 实例化
dot = graphviz.Digraph('round-table', comment='The Round Table')
# 添加节点
dot.node('A', 'King Arthur')
dot.node('B', 'Sir Bedevere the Wise')
dot.node('L', 'Sir Lancelot the Brave')
# 添加边
dot.edges(['AB', 'AL'])
dot.edge('B', 'L', constraint='false')
# 指定一个存放结果图片的文件夹
dot.render(directory='./outputdir', view=True)
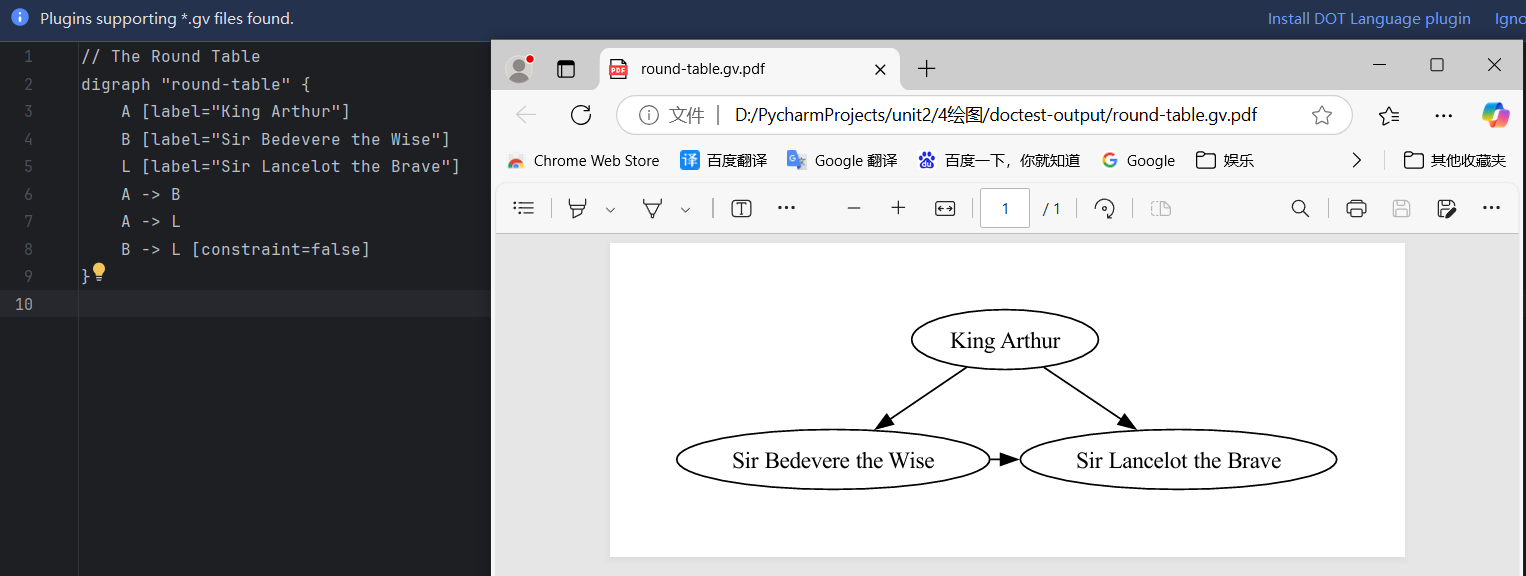
# 可在文件夹下看到配置定义源文件和生成的pdf,如果弹窗询问可以用WPS或浏览器打开pdf文件。
在输出文件夹中查看dot语法文件和图片结果
由上节课数据生成拓扑
import os
import graphviz as gv
# 添加环境变量,能正确调用graphviz程序
os.environ["PATH"] += os.pathsep + r'C:\Program Files\Graphviz\bin' # 确保与graphviz安装路径一致
# 拓扑字典,由上节课输出信息得出
topology_dict = {
('S0', 'GE0/0/1'): ('Cloud', 'GE0/0/1'),
('S0', 'GE0/0/2'): ('S1', 'GE0/0/1'),
('S0', 'GE0/0/3'): ('S2', 'GE0/0/1'),
}
# 获取所有节点
nodes = set(
[item[0] for item in list(topology_dict.keys()) + list(topology_dict.values())]
)
# 创建 Graphviz 图
graph = gv.Graph(format="svg")
# 添加节点
for node in nodes:
graph.node(node)
# 添加边
for key, value in topology_dict.items():
head, t_label = key
tail, h_label = value
graph.edge(head, tail, headlabel=h_label, taillabel=t_label, label=" " * 12)
# 渲染并保存图像
filename = graph.render(filename="./outputdir/topology")
print(f'save in {filename}')
打开topology.svg,可见结果与eNSP中拓扑完全一致。

意义:从效果上看,最终结果绕了一圈跟eNSP中拓扑图一致。但eNSP毕竟是别人的软件、和软件本身用作学习没有管理功能。代码通过搜集自家企业设备信息,可以建立自己的数据库并进行个性化的管理, 和进行个性化软件开发、例如数据大屏。
(选做)带有定义图标样式参数和方法封装的改进例子
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys
try:
import graphviz as gv
except ImportError:
print("Module graphviz needs to be installed")
print("pip install graphviz")
sys.exit()
# 关于图表绘制UI上的一些配置,如图标名字、字体颜色、线条粗细等。
styles = {
"graph": {
"label": "拓扑图",
"fontsize": "10",
"fontcolor": "white",
"bgcolor": "#3F3F3F",
"rankdir": "BT",
},
"nodes": {
"fontname": "Helvetica",
"shape": "box",
"fontcolor": "white",
"color": "#006699",
"style": "filled",
"fillcolor": "#006699",
"margin": "0.4绘图",
},
"edges": {
"style": "dashed",
"color": "green",
"arrowhead": "open",
"fontname": "Courier",
"fontsize": "14",
"fontcolor": "white",
},
}
def apply_styles(graph, styles):
""" 绘制节点、边"""
graph.graph_attr.update(("graph" in styles and styles["graph"]) or {})
graph.node_attr.update(("nodes" in styles and styles["nodes"]) or {})
graph.edge_attr.update(("edges" in styles and styles["edges"]) or {})
return graph
def draw_topology(topology_dict, out_filename="topology.svg", style_dict=styles):
"""
topology_dict - 准备的节点数据结构如下
topology_dict:
{('R4', 'Eth0/1'): ('R5', 'Eth0/1'),
('R4', 'Eth0/2'): ('R6', 'Eth0/0')}
边结构:
[ R5 ]-Eth0/1 --- Eth0/1-[ R4 ]-Eth0/2---Eth0/0-[ R6 ]
输出拓扑图为topology.svg格式
"""
nodes = set(
[item[0] for item in list(topology_dict.keys()) + list(topology_dict.values())]
)
graph = gv.Graph(format="svg")
for node in nodes:
graph.node(node)
for key, value in topology_dict.items():
head, t_label = key
tail, h_label = value
graph.edge(head, tail, headlabel=h_label, taillabel=t_label, label=" " * 12)
graph = apply_styles(graph, style_dict)
filename = graph.render(filename=out_filename)
print(f'save in {filename}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 添加环境变量,能正确调用graphviz程序
import os
os.environ["PATH"] += os.pathsep + r'C:\Program Files\Graphviz\bin'
# 课上eNSP三个节点,通过lldp发现后得到的数据,保存到json本地文件。然后整理成易于绘图库使用的特定格式,下面的字典每一项键值对都是元组,每一个元组的两项为设备名和网口编号。
# ['Local Intf Neighbor Dev Neighbor Intf Exptime',
# 'GE0/0/1 - 0a00-2700-0009 3345 ',
# 'GE0/0/2 S1 GE0/0/1 109 ',
# 'GE0/0/3 S2 GE0/0/1 98 ']
topology_dict = {
('S0', 'GE0/0/1'): ('Cloud', 'GE0/0/1'),
('S0', 'GE0/0/2'): ('S1', 'GE0/0/1'),
('S0', 'GE0/0/3'): ('S2', 'GE0/0/1'),
}
draw_topology(topology_dict)